The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and with it, the threats that lurk within. Cybercriminals are becoming increasingly sophisticated, developing advanced tactics to steal data, disrupt operations, and exploit vulnerabilities. This poses a significant challenge for individuals and organizations alike, demanding a proactive approach to cybersecurity.
You can enlist the help of a managed IT services company in Calgary or elsewhere to ensure that you’re working in a security-conscious manner. Network security is becoming increasingly important and it’s therefore important to locate any potential attackers and decrease the chance of your network becoming compromised.
The Rise of the Evolving Threat: Why We Need to Be Worried
-
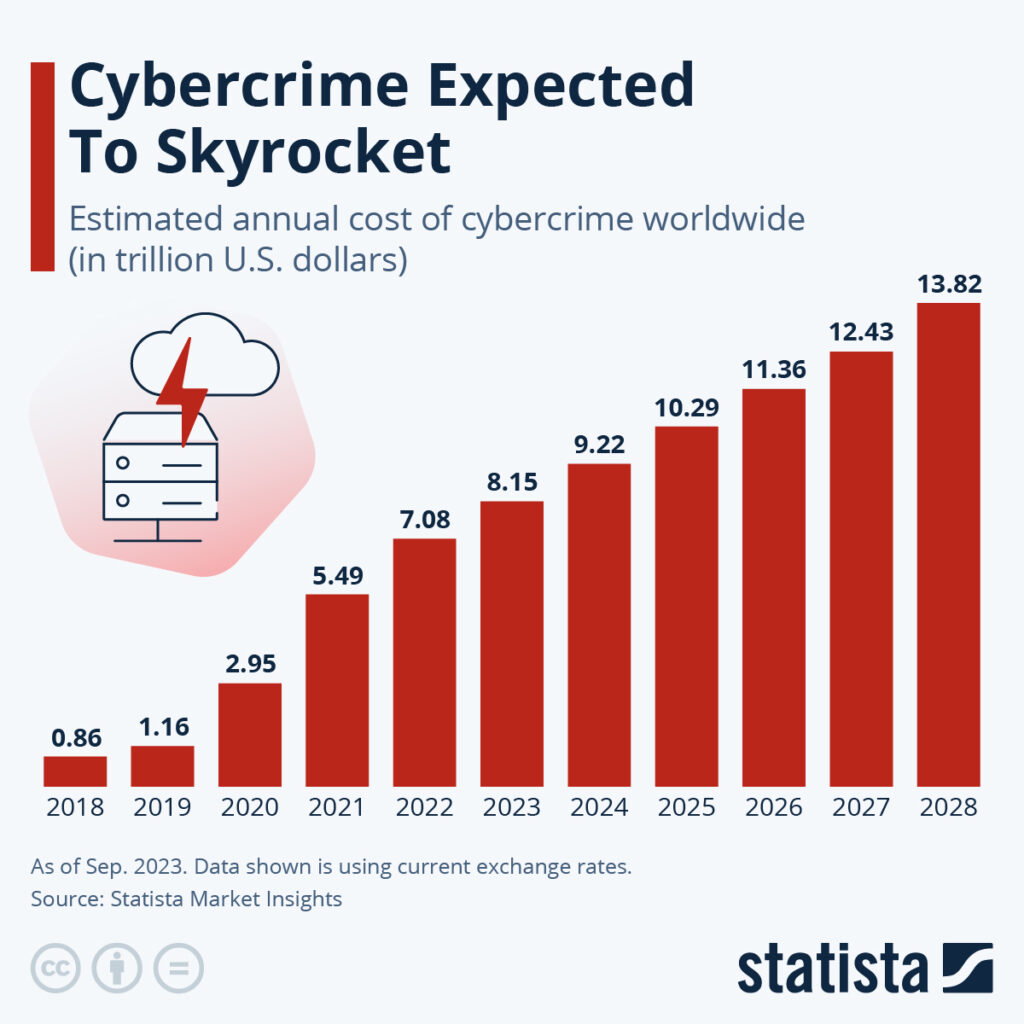
Increased Financial Motive: Cybercrime is a booming business, with estimated global costs reaching $10.5 trillion by 2025 [Source: Embroker]. This financial incentive drives criminals to develop more intricate methods for financial gain.
-
Nation-State Actors: Beyond financial motives, cyberattacks are used by nation-states for espionage, disrupting critical infrastructure, and influencing political processes. These well-funded actors often possess highly skilled hackers.
-
AI and Machine Learning: The integration of AI and machine learning in cyberattacks is a growing concern. Criminals leverage these technologies to automate tasks, personalize attacks, and identify vulnerabilities with greater efficiency.
A Multifaceted Threat Landscape: A Look at Common Cyberattacks
Cyberattacks come in various forms, each targeting different aspects of a system’s security. Here’s a breakdown of some prevalent threats:
| Threat Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Phishing: Deceptive emails or messages designed to trick users into revealing sensitive information. | A seemingly legitimate email from a bank requesting login credentials. | |
| Malware: Malicious software that infiltrates a system to steal data, disrupt operations, or install ransomware. | Ransomware that encrypts files, demanding payment for decryption. | |
| Social Engineering: Exploiting human psychology to manipulate victims into compromising security measures. | A phone call impersonating a tech support representative, prompting remote access. | |
| Zero-Day Attacks: Exploiting previously unknown vulnerabilities in software or hardware. | Targeting a newly discovered flaw in a widely used operating system. | |
| Supply Chain Attacks: Compromising a trusted third-party vendor to gain access to their customers’ systems. | Hacking a software provider to inject malicious code into their product. |
Cyber criminals are constantly refining their techniques. Here are some emerging trends to be aware of:
-
Deepfakes and Voice Mimicry: Using AI-powered tools to create realistic audio and video for more convincing social engineering attacks.
-
IoT (Internet of Things) Exploitation: Targeting vulnerabilities in interconnected devices within homes and businesses to gain access to networks.
-
Cloud-Based Attacks: Focusing on weaknesses in cloud infrastructure platforms to steal data stored by organizations.
Staying Ahead of the Curve: Practical Steps to Enhance Your Cybersecurity Posture
While the threat landscape is evolving, individuals and organizations can take proactive steps to strengthen their defenses:
-
Regular Software Updates: Patching vulnerabilities in operating systems, software, and firmware is crucial to address known security gaps.
-
Strong Passwords & Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement complex passwords and enable MFA to add an extra layer of security to login attempts.
-
Employee Training: Regularly educate employees on cyber threats and best practices for secure online behavior.
-
Data Backups: Maintain regular backups of critical data to ensure recovery in case of a cyberattack.
-
Cybersecurity Software: Utilize security software such as antivirus, anti-malware, and firewalls to detect and prevent threats.
Additionally, organizations should consider:
-
Security Awareness Programs: Foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness within the organization, encouraging employees to report suspicious activity.
-
Penetration Testing: Conduct simulated cyberattacks to identify vulnerabilities and improve defense mechanisms.
-
Incident Response Plan: Develop a clear plan for responding to a cyberattack, minimizing downtime and data loss.
For organizations operating in regulated industries or those handling sensitive data, partnering with cybersecurity professionals who understand specific compliance requirements can be invaluable. Companies similar to Blue Goat Cyber and other specialized consultants can provide tailored security assessments and help navigate complex regulatory landscapes while ensuring comprehensive protection.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Fight for Cybersecurity
The battle against cyber threats is a continuous process. As attackers adapt, so must our defenses. By staying informed, implementing robust security practices, and fostering a culture of awareness, we can mitigate the risks and navigate the ever-evolving digital landscape with greater confidence.